Definition of social cost – Social cost is the total cost to society. It includes both private costs plus any external costs.
The social costs of smoking include the passive smoking that other people experience.
The social cost involved in building and running an airport can be split up into:
Private costs of airport
External Cost of airport
- Noise and air pollution to those living nearby.
- Risk of accident to those living nearby.
- Loss of landscape.
Importance of Social Cost
Rational choice theory suggests individuals will only consider their private costs. For example, if deciding how to travel, we will consider the cost of petrol and time taken to drive. However, we won’t take into consideration the impact on the environment or congestion levels for other members in society.
Therefore, if social costs significantly vary from private costs then we may get a socially inefficient outcome in a free market.
Marginal Social Cost (MSC)
The cost to society of producing / consuming one extra unit of output.
| Q | MPC | MXC | MSC |
| 1 | 5 | 3 | 8 |
| 2 | 6 | 3 | 9 |
| 3 | 7 | 3 | 10 |
| 4 | 8 | 3 | 11 |
| 5 | 9 | 3 | 12 |
Diagram showing marginal social costs
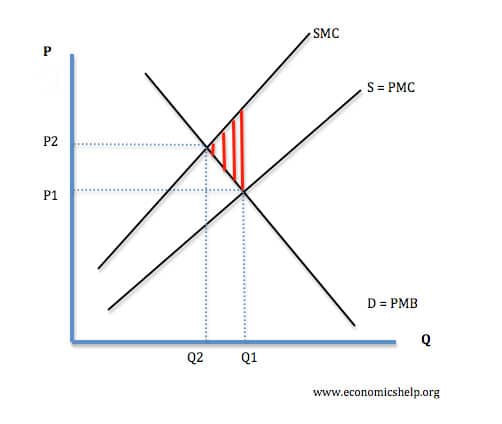
For goods with negative externalities the social cost is greater than the private cost.