In the lab, you will be spending a few days, dissecting the frog. Periodically, your instructor may pause to show you illustrations, diagrams or videos of procedures. This page is additional information that may be given to you in class as you perform the dissection.
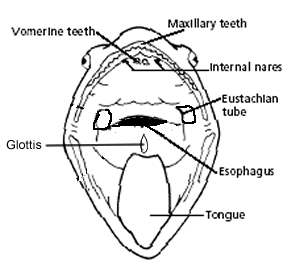
Vomarine and Maxillary Teeth: Used for holding prey
Internal Nares (nostrils) breathing
Eustachian Tubes: equalize pressure in inner ear
Glottis : Tube leading to the lungs
Esophagus: Tube leading to the stomach
Tongue: Front attached, aids in grabbing prey
Tympanic Membrane: eardrum, located behind eyes
Nictitating Membrane: clear eyelid, protects the eye
Internal Nares (nostrils) breathing
Eustachian Tubes: equalize pressure in inner ear
Glottis : Tube leading to the lungs
Esophagus: Tube leading to the stomach
Tongue: Front attached, aids in grabbing prey
Tympanic Membrane: eardrum, located behind eyes
Nictitating Membrane: clear eyelid, protects the eye
Handouts on the Frog Dissection:
Frog External Anatomy
Frog Digestive and Urogenital System
Frog Brain and Bones
Frog Digestive and Urogenital System
Frog Brain and Bones
The Mouth
The Organs of the Abdominal Cavity
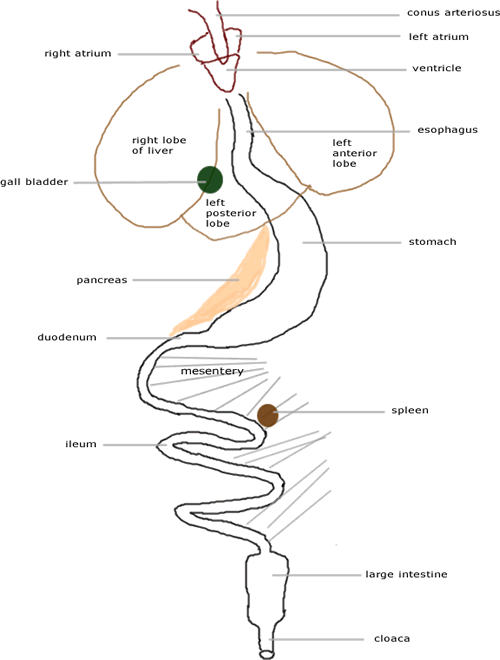
Peritoneum: Spiderweb like membrane that covers organs
Stomach: First site of chemical digestion, breaks down food
Liver: Makes bile (aids in digestion)
Gall bladder: Stores bile
Esophagus: Tube that leads to the stomach
Pancreas: Makes insulin (aids in digestion)
Small Intestine (duodenum and ileum): absorb nutrients from food
Mesentery: Holds coils of the small intestine together
Mesentery: Holds coils of the small intestine together
Large Intestine: Collects waste, absorbs water
Cloaca: "Sewer": eggs, sperm, urine and feces enter this area
The Urogenital System
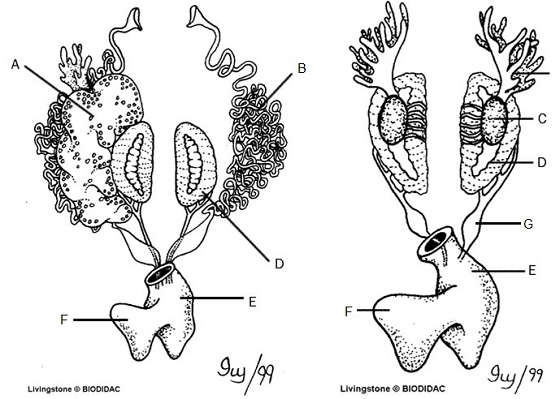
Kidneys (D): Filter Blood
Ureters (G): Carry urine from kidneys to bladder
Testes (C): Make sperm
Oviducts (B): eggs travel through these
Ovary: makes eggs (A) - ovary is often too small to see, but eggs are visible
Urinary Bladder (F): Stores Urine
Cloaca (E): Where sperm, eggs, urine, and feces exit.