We now need to present both stock (asset market) and flow (commodity market) equilibrium on the same graph. The conventional way to do this is to put the real interest rate on the vertical axis and output (income and employment) on the horizontal one. First, we present again the equations of stock and flow equilibrium.
The conditions of asset (stock) and goods market (flow) equilibrium as presented in the previous topic are, respectively
1. M/P = γ − θ ( r + τ ) + ε Y
and
2. Y = ( a + δ + ΦBT + DSB)/(s + m) − μ/(s + m) r + m* /(s + m) Y* − σ/(s + m) Q
where we express the domestic interest rate simply as r without regard to the role of world capital market conditions in determining it---that will be incorporated later. If you are not completely familiar with the derivation and meaning of these equations you should review the previous two topics again.
The combinations of r and Y for which Equation 2 holds can be presented as a negative relationship between income and the real interest rate as shown in Figure 1. The downward sloping flow-equilibrium curve---normally not a straight line as here portrayed---is called the IS curve in textbooks and we will follow that naming convention here.
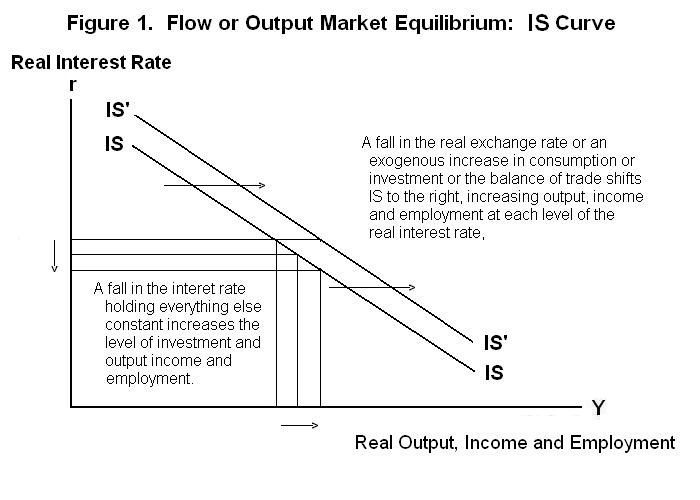
A fall in the interest rate leads to an expansion of investment, causing equilibrium output, income and emloyment to increase as we move down along the IS curve. A fall in the real exchange rate shifts world demand onto domestic goods, increasing income at each level of the real interest rate and shifting IS to the right. An increase in rest-of-world income, or exogenous increase in consumption or investment or net exports at any given level of the real interest rate also causes the IS line to shift to the right and the equilibrium level of output, income and employment to increase.
To portray asset equilibrium in terms of the relationship it implies between the real interest rate and the level of income, it is useful to rearrange Equation 1 to put r on the left side:
1a. r = − (1/θ) M/P + γ/θ − τ + (ε/θ) Y
Since ε/θ in this equation is preceded by a positive sign, the equation defines a positive relationship between the real interest rate and level of income, holding everything else constant, and can be portrayed as the upward sloping curve LM (portrayed as a straight line) in Figure 2. (The name LM, meaning liquidity-money, is also traditional.) The LM curve gives the combinations of income and the interest rate for which the demand for money (or desired liquidity) equals the money supply and hence for which the domestic economy is in asset or stock equilibrium.
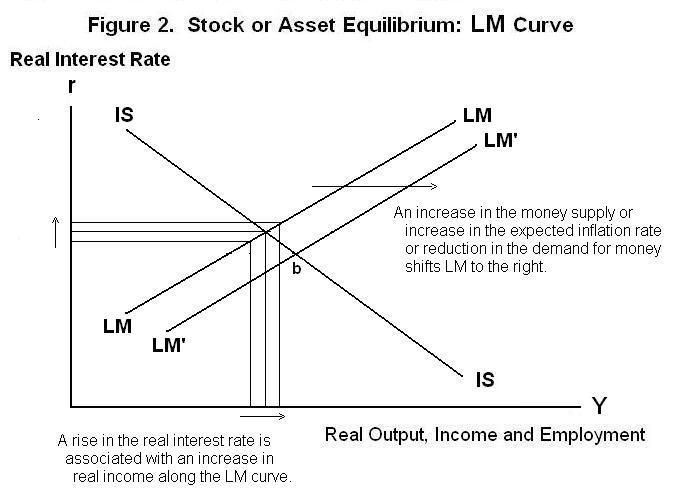
An increase in the money supply holding the real interest rate constant requires a higher level of income to make the demand for money equal to that greater supply, shifting LM to the right. The combinations of income and the real interest rate at which the demand for money equals the supply now lie farther to the right. An increase in the expected inflation rate at a given level of the real interest rate increases the cost of holding money and reduces the quantity people chose to hold. This requires that the level of income rise at the given world real interest rate to bring desired money holdings back into line with the unchanged money supply and preserve asset equilibrium---the LM curve shifts to the right. Overall equilibrium will occur where the IS and LM curves cross. In a an economy that is closed to international trade, an increase in the money supply in Figure 2 will shift LM to the right causing the interest rate to fall as the public tries to reestablish portfolio equilibrium by purchasing assets. The fall in the interest rate will cause output, income and employment to increase. The interest rate will fall and income will increase until the quantity of money demanded has increased by an amount equal to the increase in the money supply. The new equilibrium will be at point b in Figure 2.
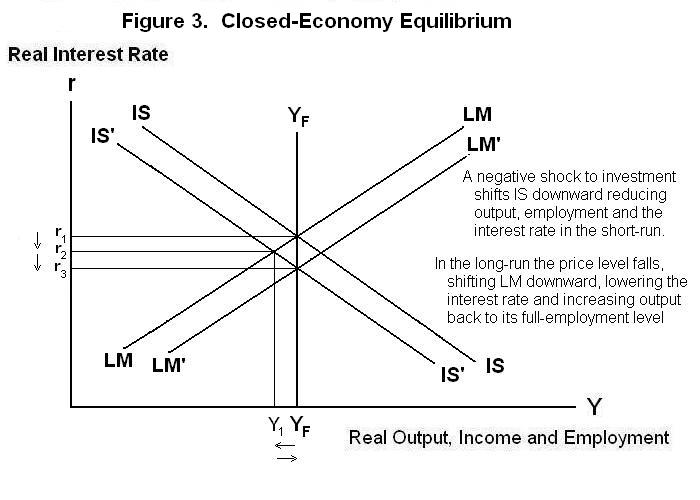
Full portrayal of equilibrium also requires that we add a vertical line YF to portray the full-employment level of income which the equilibrating process will eventually achieve in the long-run. This is shown in Figure 3.
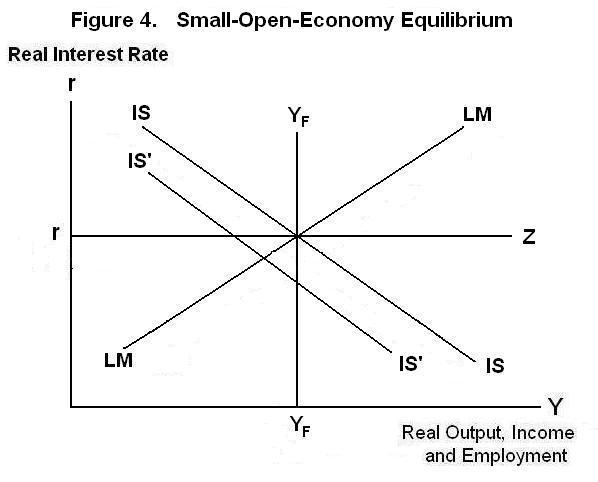
The above analysis assumes, unrealistically, that our economy is closed to international trade and capital movements. When we incorporate these elements an additional line has to be added to the graph---the horizontal rZ line in Figure 4.